Those familiar with the construction industry know pre-engineered buildings are way better than conventional (traditional) buildings. While PEB offers the flexibility of assembling the prefabricated parts, the conventional buildings need to be constructed on-site by employing several elements.
However, a few things that are somewhat common between the two – designing, preparing a strong foundation, framing, and finishing. Still, easy assembly, quick erection, and execution make PEB a clear winner between pre-engineered building vs conventional building.
To prove our point we have compared the two on 11 checkpoints and formed a tabular presentation for your quick review.
Pre-Engineered Building Vs Conventional Building – Why PEB won hands down?
Pre-engineered building (PEBs) straightaway cut the cost. It doesn’t require you to hire an architect or a designer, moreover, PEB structures are flexible, efficient, and known for seamless construction. The basic ideology behind prefab structures is that the components are fabricated individually in a factory, delivered onsite, and assembled using nuts and bolts.
As a result, the pre-engineered buildings have a fast turnaround time and can be prepared in less than 8 weeks. On the other hand, preparing conventional buildings is a kind of messy process which requires complex designing, laying the foundation from scratch, a long construction process, and way costlier than PEBs. Here is what differs Pre-Engineered Buildings and Conventional Buildings.
11 Differences between Pre-Engineered Buildings and Conventional Buildings
| Checkpoints | Properties | Pre-Engineered Buildings | Conventional Steel Building |
|---|---|---|---|
| Checkpoint 1 | Structural Weight | Pre-engineered buildings incorporate efficient and well-thought
use of steel which makes them 30% lighter than conventional buildings |
Conventional steel buildings comprise heavy steel rods which makes
the overall structure very heavy, more than needed. |
| Checkpoint 2 | Design | The structure of PEBs is designed with the latest software and
architectural techniques. Thus, bring out some of the amazing and innovative designs into existence. |
Conventional steel buildings do not leave much scope for
innovation and design. It involves slight modification in traditional designs to make it look new.. |
| Checkpoint 3 | Construction Period | Thirdly, and most importantly, the process of construction is fast
and takes on an average of 6 to 8 weeks |
Above all, the conventional building takes around 20 to 26 weeks
to complete. |
| Checkpoint 4 | Foundation | Lightweight and strong. | A heavy foundation is required. |
| Checkpoint 5 | Erection and Simplicity | The connections are normally standard. Therefore, the time for the
erection of the building is faster. |
The connections are complex and different every time. Thus it
takes time for the erection of the building. |
| Checkpoint 6 | Erection Time and Cost | Pre-engineered buildings are pre-planned. Their erection process
is fast and less workforce is required. Also, because of light weightedness, it does not require machinery. |
It is 20% more expensive than PEB and requires extensive labor and
heavy machinery. Therefore, The erection process is slow. |
| Checkpoint 7 | Seismic Resistance | The use of flexible frames offers resistance from SEismic
forces. |
Frames used in conventional buildings are rigid and do not offer
resistance from seismic forces. |
| Checkpoint 8 | Overall Cost | It is a cost-effective solution. Usually costs 30% less than
conventional buildings. |
Higher costs |
| Checkpoint 9 | Architecture | New architectural designs can be built | Less to no scope of innovation in terms of architectural
designs. |
| Checkpoint 10 | Future Expansion | Expansion of building is very easy | On the other hand, expansion is complex and costly. |
| Checkpoint 11 | Safety and Responsibility | The responsibility of safety is on one supplier who worked
throughout the project. |
It is a question of concern since many suppliers and contractors
are involved. |
Essential Components of Pre-Engineered Buildings
The Pre-engineered building structures are basically divided into 4 major components that together make the structure robust and durable. Its worldwide adaptability is the reason for its increased popularity.
Let us walk you through all the components one by one and understand what makes pre-engineered buildings the first choice of pre-engineered building manufacturers.
Primary components of pre-engineered buildings
The Primary components of any pre-engineered building structure consist of 3 parts – Mainframe, Column, and Rafter.
- Mainframe
The mainframe is like the skeleton in a human body. It is a rigid steel structure made of strong steel rods providing the overall strength to the building. The frame comprises tapered columns and tapered rafters. Different shaped beams or flanges are webbed together using continuous fillet weld on one side to disburse stress throughout the channel.
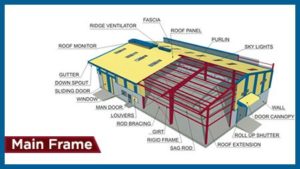
- Columns
Columns are basically vertical pillar-like structures that increase in width as they go from the bottom to the top of the buildings. These structures provide strength and transfer the pressure through the vertical loads to the foundation. Pre-engineered building manufacturers make columns of I sections that are more economical than others. The image given below shows the columns used in the construction of pre-engineered buildings.

- Rafters
Typical rafters as shown in the image are sloped structural beams that give strength and support to the roof deck and the loads associated with it. The beam is placed between the ridge or hip to the wall plate, downslope perimeter, or eave.

Secondary Components of pre-engineered buildings
Secondary structure components are basic parts that give support to the roof in addition to the walls. This includes Purlins, Grits, Bracings, and Eave struts.
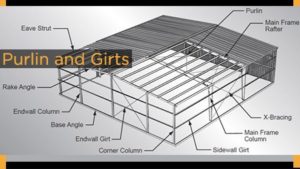
- Purlins and Girts
Purlins are the secondary components used to support the roof. However, Grits are the secondary components used on the walls whereas Eave struts are used in the middle of the sidewall and the roof at the intersections.
Purlins and girts shall be cold-formed “Z” sections with stiffened flanges.
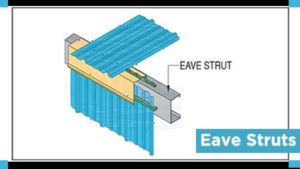
- Eave Struts
Eave struts shall be cold-formed “C” sections with unequal flanges. Dimensions of Eave struts are 200 mm deep with a 104 mm wide top flange, a 118 mm wide bottom flange, both are formed parallel to the roof slope. Each flange has a 24 mm stiffener lip.
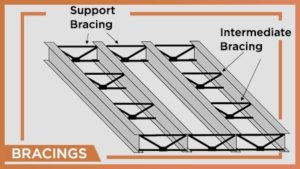
- Bracings
Forces applicable in the longitudinal direction are also important to consider as they can weaken the structure with time. Moreover, these forces are generally natural like wind, earthquakes, etc. Diagonal Bracings in the roof and side walls ensure that the building stands against these longitudinal forces.
3. Sheeting or Cladding
Construction of pre-engineered buildings in India involves the use of sheets made up of base metal Galvalume coated steel conforming to ASTM A 792 M grade 345B or aluminum conforming to ASTM B 209M. This, in turn, protects the complete building from the above, by controlling harmful rays and controlling other environmental factors in control.
4. Accessories
In addition to steel material, the other parts that help in providing a finish to the building are turbo ventilators, skylights, doors and windows, roof curbs, and fasteners, and other non-structural elements known as a+ccessories of the pre-engineered buildings.
Where Pre-Engineered Buildings can be used?
Today pre-engineered buildings are gaining a lot more popularity in many parts of India and the western world. As per the stats, the last two years saw a rising demand for PEBs, and the numbers are expected to exponentially. Here, we have enlisted a few building structures which can be easily built using PEBs.
- Houses & Living Shelters
- Factories
- Warehouses
- Auditoriums
- Supermarkets
- Workshops
- Office Buildings
- Petrol Pumps/Service Buildings
- Schools
- Community centers and much more.
HRS Infrastructure- The leading pre-engineered buildings manufacturer
The pre-engineered building technique is the revolutionary way to meet the surging Indian infrastructure demand. It consumes less time, provides flexibility to move the structures from one place to another, is cost-effective and highly durable. All these traits and 11 checkpoints make pre-engineered structures preferred over the conventional buildings. The HRS Infrastructure is a leader in designing and installing PEBs. So, if you are looking for the best and quick solution to install a factory or any other complex metallic structure then connect with the experts today!

